E. complanata exhibits a peristaltic locomotion pattern common to elongated, segmented polychaetes (Pardo and Amaral, 2005). This method utilizes alternating contractions of the longitudinal and circular muscles, to provide forward movement of parapoida. The contraction of the circular muscles elongates or extends the parapodia and setae; which are then anchored by the shortening contractile movement of the longitudinal muscles, allowing forward movement(Pardo and Amaral, 2005; Ruppert et al, 2004; Figure 1).
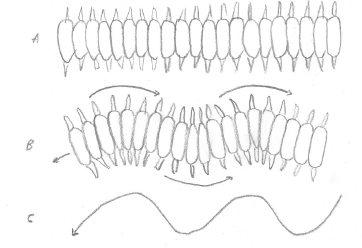
Figure 1. Peristalic movement of E. complanata. A depicts the animal at 'rest'. B depicts the peristalitic pattern of locomotion. C represents the path of movements this locomotion pattern creates. |